Table of Contents
Two popular investment vehicles are stocks and mutual funds. While mutual funds are a collection of stocks, bonds, or other assets managed by a qualified fund manager, stocks are ownership shares in a firm.
Investing is essential to grow your wealth and achieve your financial goals. However, with so many investment options available, deciding where to put your money can take time and effort.
We will explore the distinctions between these two types of investment vehicles as well as their advantages and disadvantages.
We will also discuss essential factors to consider when making investment decisions, such as risk tolerance, investment goals, time horizon, fees, and diversification.
Stocks vs. Mutual Funds. What are mutual funds?
Stocks, also known as equities, represent ownership in a company. When you purchase a stock, you become a partial owner of the business and are entitled to share in its profits and assets.
A stock’s value may rise or fall depending on a number of variables, including the company’s financial success, industry trends, and broader economic conditions.
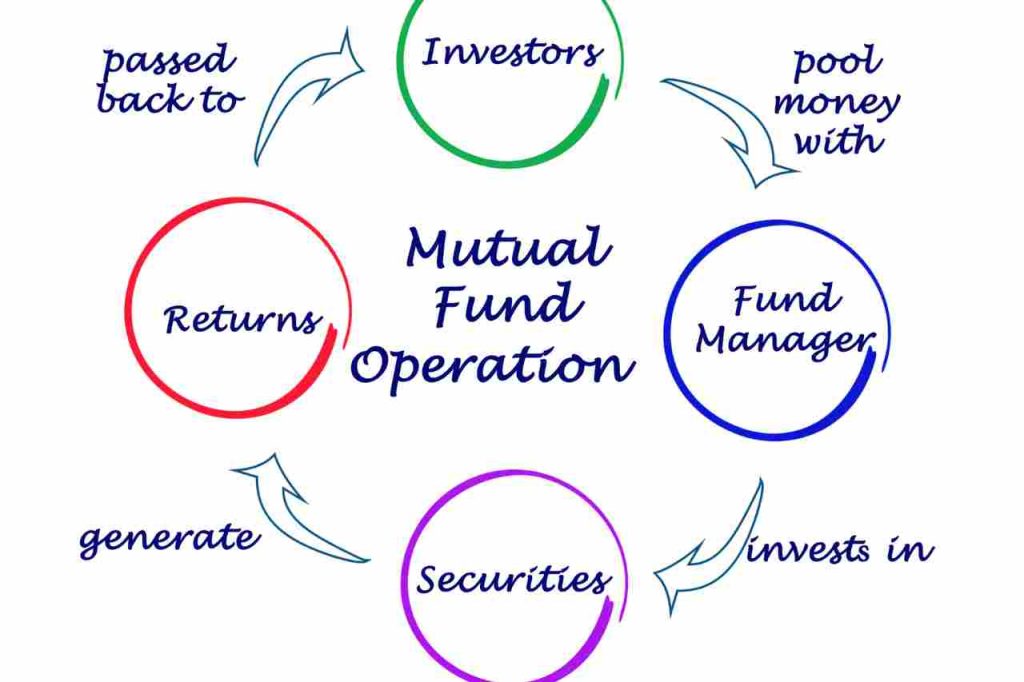
The usage of mutual funds, a distinct kind of investment vehicle, allows the money from several investors to be pooled in order to purchase a wide portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets.

By investing in a mutual fund, you indirectly own a portion of the underlying assets. Investment experts that manage mutual funds choose which assets to acquire and sell depending on the goal and plan of the fund’s investments.
One of the main differences between stocks and mutual funds is the level of diversification.
When you buy an individual stock, your investment is concentrated in one company. If that company performs poorly, your investment could suffer. In contrast, mutual funds hold a basket of securities, which can help spread risk and reduce the impact of any security’s performance on the overall portfolio.
Another difference is the level of control. When you invest in stocks, you have full control over your individual investments.
You can choose which companies to invest in, when to buy and sell, and how much to invest. With mutual funds, you relinquish some of that control to the fund manager, who makes investment decisions on your behalf.
There are also differences in fees and expenses. When you buy individual stocks, you typically pay a commission fee to your broker. With mutual funds, you pay an expense ratio covering the fund’s operating costs and management fees.
Generally, stocks represent ownership in individual companies, while mutual funds are investment vehicles with a diversified portfolio of securities. Stocks offer more control over individual investments, but mutual funds provide diversification and professional management.
Factors to Consider
When choosing between mutual funds and equities to invest in, there are several factors you should consider to help guide your decision.
These factors include:
Risk Tolerance
When determining whether to invest in stocks or mutual funds, risk tolerance is an important consideration.
It refers to your willingness to take on investment risk, and it can vary depending on your circumstances, such as your age, income, and investment goals.
Individual stocks may provide the possibility of significant profits but also come with a greater degree of risk, so you could feel at ease investing in them if you have a high tolerance for risk.
In contrast, if you have a low-risk tolerance, you may prefer investing in mutual funds, which are less risky due to their diversified portfolios.
To determine your risk tolerance, consider your investment goals, time horizon, and financial situation.
For example, if you are young and have a long time horizon, you may be more willing to take on risk, as you have time to recover from any short-term losses.
However, if you are approaching retirement and have a shorter time horizon, you may prefer to invest in less risky assets, such as bonds or mutual funds that invest in dividend-paying stocks.
Investment Goals
Your investment goals are another important factor when deciding whether to invest in stocks or mutual funds.
Your investment goals may include long-term growth, generating income, or preserving capital.
Here are some ways that stocks and mutual funds can help you achieve different investment goals:
Long-Term Growth: If your goal is to achieve long-term growth, investing in stocks may be a better option. Historically, equities have outperformed other asset classes in terms of long-term returns. Diversifying your portfolio is crucial to lowering risk since investing in individual equities may be dangerous.
Generating Income: If your goal is to generate income, mutual funds that invest in dividend-paying stocks or bonds may be more suitable. For retirees or those who are in the process of retiring, these kinds of mutual funds may provide a reliable source of income.
Preserving Capital: If your goal is to preserve capital, investing in less risky assets, such as bonds or mutual funds that invest in high-quality fixed-income securities, is a better option. These types of investments may provide lower returns but carry lower risk.
Time Horizon
It refers to the length of time you plan to hold your investments. It is important to consider when deciding whether to invest in stocks or mutual funds because different types of investments are better suited to different time horizons.
Investing in stocks may be a wise choice if you have a longer time horizon, such as 10 or 20 years, since historically, equities have produced larger returns over the long run. Diversifying your portfolio is crucial to lowering risk since investing in individual equities may be dangerous.
If you want to invest for a shorter period of time, say five years or fewer, mutual funds could be a better option.
Mutual funds are typically less volatile than individual stocks and are already diversified across a range of securities, which can help reduce risk.
Mutual funds might also be a smart choice if you require quick access to your money since they tend to be more liquid than individual equities.
Fees and Expenses
Fees and expenses are another important factor when deciding whether to invest in stocks or mutual funds. Both types of investments come with fees and expenses, but the amount and structure of these costs can vary significantly.
When you invest in individual stocks, you typically pay a commission or trading fee each time you buy or sell a stock.
Additionally, if you work with a broker, you may need to pay an annual account maintenance fee or other fees for services like research or portfolio management.
An expense ratio, which is a charge that covers the fund’s operational costs, including management fees, administrative charges, and other expenditures, is often paid when you invest in mutual funds.
The cost ratio may vary greatly depending on the fund and is normally quoted as a percentage of your investment.

When considering whether to invest in stocks or mutual funds, it’s critical to carefully evaluate fees and costs.
While investing in individual stocks may offer lower fees in some cases, it can also be riskier and require more time and effort to manage your portfolio.
In contrast, investing in mutual funds may offer more diversification and professional management, but it can also come with higher fees and expenses.
Diversification
Diversification is another essential factor when deciding whether to invest in stocks or mutual funds.
To lower risk, diversification means distributing your assets across a range of industries, geographies, and asset classes.
Investing in individual stocks can be challenging to achieve a high level of diversification because you would need to invest in many different stocks to achieve adequate diversification.
Additionally, investing in personal stocks can be risky because the performance of any stock can significantly impact your portfolio’s overall performance.
When you invest in mutual funds, however, you can achieve a high level of diversification more easily because mutual funds invest in various stocks or other securities.
For example, a mutual fund that tracks a broad market index may invest in hundreds or thousands of different stocks, providing a high level of diversification with just one investment.
Diversification can reduce risk and increase the likelihood of achieving your investment goals over the long term.
By diversifying your holdings across a range of securities and asset types, you can help protect against market volatility and reduce the impact of any one investment on your portfolio.
Benefits of Investing in Stocks
Investing in stocks can offer several potential benefits, including:
Potential for higher returns
Over the long run, stocks have traditionally outperformed other asset classes in terms of returns. While stocks can be volatile in a short time, over the long term, they have provided higher average returns than bonds, cash, or other investments.

Ability to own individual companies
When you invest in individual stocks, you can own a piece of a specific company. This can appeal to investors who want to support specific companies or are interested in the potential growth of a particular industry or sector.
Control over your investments.
When making an individual stock investment, you have greater control over your investments than you would with mutual funds or other types of investments. You can choose which companies to invest in and buy and sell stocks at any time.
Flexibility
Investing in stocks can be flexible, as you can choose how much money to invest and when to buy or sell stocks. This can appeal to investors who want to be more involved in managing their investments.
Potential tax benefits
Depending on your investment strategy and the type of account you use to invest in stocks, you can take advantage of tax benefits such as capital gains, tax deferral, or tax-free withdrawals.
While there are benefits to investing in stocks, it’s important to remember that investing in individual stocks can be risky and requires significant research and due diligence. Additionally, investing in stocks can be time-consuming, requiring ongoing monitoring and management.
Benefits of Investing in Mutual Funds
Investing in mutual funds can offer several potential benefits, including:
Diversification
By distributing your assets across several asset classes, industries, and geographical areas, mutual funds, which invest in a variety of securities, may help you lower your risk.
This can appeal to investors who want to achieve a high level of diversification with just one investment.
Professional management
They are run by qualified fund managers who choose investments on behalf of the fund’s shareholders.
This can appeal to investors needing more time, expertise, or resources to manage their investments.

Lower transaction costs
Because mutual funds buy and sell securities in large quantities, they can often do so at lower transaction costs than individual investors.
This can reduce the overall fees and expenses of mutual funds.
Flexibility
Mutual funds can be purchased in different share classes, offering flexibility in fees and expenses.
Additionally, mutual funds can be purchased through various account types, such as individual retirement accounts (IRAs) or 401(k) plans, which can offer tax advantages.
Liquidity
Investors may immediately access their money and have liquidity thanks to the daily buying and selling of mutual funds.
While there are advantages to investing in mutual funds, it’s vital to keep in mind that there are dangers involved as well.
Like any investment, mutual funds can fluctuate in value, and fees and expenses are associated with investing in mutual funds.
Additionally, while professional management can be an advantage, not all fund managers perform equally well, and previous results might not always predict future outcomes.
How to Choose
Investing in stocks or mutual funds ultimately depends on your financial situation, investment goals, and risk tolerance. Here are some steps to consider when deciding which option is right for you:
Determine your investment goals
Consider what you’re investing for and how much risk you will take. If you’re investing for retirement or a long-term goal, you may be more comfortable taking on higher risk and investing in stocks.
Mutual funds may be a better option if you’re investing for a shorter-term goal or are more risk-averse.

Assess your risk tolerance.
Determine how much risk you’re willing to take on. Stocks can be more volatile than mutual funds, making them riskier but offering higher potential returns.
Mutual funds may be a better option if you’re uncomfortable with the potential for significant losses.
Consider your time horizon.
Think about how long you plan to invest. Stocks may be more appropriate for long-term investments, while mutual funds may be better for shorter-term investments.
Evaluate fees and expenses.
Consider the fees and expenses associated with both options. Mutual funds can have higher fees and expenses than investing in individual stocks, but they also offer professional management and diversification.
Do your research
Whether you’re considering investing in stocks or mutual funds, it’s essential to research and understand the risks and potential rewards associated with each option.
Consider reading investment books or articles, consulting with a financial advisor, or researching online before making investment decisions.
Conclusion
Depending on your investment objectives, risk tolerance, and personal preferences
, you may choose to invest in stocks rather than mutual funds.
While stocks have a large potential return, they also carry greater risks and need more study and analysis.
Mutual funds, on the other hand, provide diversification and professional management but come with higher fees and lower potential returns.
Ultimately, it’s essential to research, consult a financial advisor, and decide on an investment plan that supports your long-term financial objectives. Investing is a marathon, not a sprint, keep that in mind, and having a well-diversified portfolio to mitigate risk and maximize returns over time is essential.










